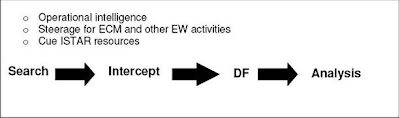
There are 3 main functions associated with ESM and they are shown along with the 4 sub-divisions of the ESM process: search, intercept, direction finding (DF) and analysis. The end product of this process will provide vital information and intelligence on the adversary, such as the establishment of an adversary’s EOB, strengths, weaknesses, dispositions, reactions and intentions.
Search
Search involves the reconnaissance of the EM spectrum for adversary emissions. An experienced EW operator will scan through the EM spectrum having already been informed on targets (transmissions) of interest to the J2 Intelligence Staff. Upon detection of a target of interest, the frequency will be passed to an EW intercept operator for further exploitation. Although this process can be quite slow, modern automated wide-band search receivers have now made it possible to scan portions of the Radio Frequency (RF) spectrum to identify active targets of interest.
The intercept process further classifies the emission by both its external characteristics (RF, modulation etc) and the internal information if available. If the emission is encrypted, very little internal information is likely to be available. The EW intercept operator will log as much information as possible extracting all potential intelligence. A transmission using clear voice will have a log of its activity made by the EW intercept operator detailing what was said, however when done live, it is very unlikely that full (verbatim) copy will be possible. Realistically, the EW intercept operator ill log or “gist” only the most relevant information (locations, intentions, reactions etc) but good practice is to make a recording that allows further extraction of information following a full transcript of the activity in slower time.
Direction Finding (DF)An emitter’s location can be obtained using the DF technique. This involves measuring the bearing at which the target signal arrives at a specialist EW DF receiver. If only one DF station is used then a line of bearing (LOB) is produced. This will provide only the direction to the transmitter but will not actually locate the target unless the distance from the DF sensor is known, which is unlikely. Two DF sensors will provide a better indication of where the target transmitter is located; however it is best practice to deploy 3 or more sensors to provide a fairly accurate location of the target. This is called Position Fixing (PF). When 3 or more sensors each provide their LOB, an ellipse can be drawn on a map, in which there is an approximate 90% chance the target is located.
Optimum accuracy of a DF system is approximately 1 degree, however at longer distances accuracy can vary up to 3 degrees and even more at the very limit of the target being audible. At distances of 30-50 km the target location ellipse will be quite large and this precludes DF being used for Target Acquisition. However, even at 3 degrees variation, DF is useful to cue other ISTAR resources to determine a more accurate target location. Figs 7 and 8 below show a typical land-based EW deployment of 4 DF sensors attempting to PF an enemy transmission and an aircraft attempting the same PF using a “rolling” baseline
 Direction Finding & Position Fixing
Direction Finding & Position Fixing
 Aircraft Direction Finding & Position
Aircraft Direction Finding & Position
Analysis of EM emissions is carried out for multiple objectives, which include:
· . Adversary’s intentions
· . Adversary’s response to own or friendly Information Operations (INFO OPS)
· . Affects of own or friendly ECM operations
· . Establishment of a comprehensive EOB
· . Targeting for kinetic action
The analysis of traffic collected by ESM sensors should, if at all possible, be fused with other intelligence Sources and Agencies (SANDA). There is a “special” relationship between EW and SIGINT and product from both can be similar and complimentary, but fusing Imagery Intelligence (IMINT) and / or Human Intelligence (HUMINT) for example, will give much greater granularity and credibility to the information derived from the ESM intercept and DF. The fusion of all the information by the J2 All Sources Cell (ASC) can provide crucial intelligence to the J3 Staff in order to allow the Commander to make key decisions.
No comments:
Post a Comment